What is BCID2?
The BioFire® FilmArray® Blood Culture Identification Panel (BCID) 2 is a test used to rapidly identify pathogens by amplifying DNA through PCR. This laboratory method helps identify organisms and resistance genes from positive blood cultures. Table 1 lists the bacterial and fungal pathogens, and resistance genes detected by the BCID2 panel.
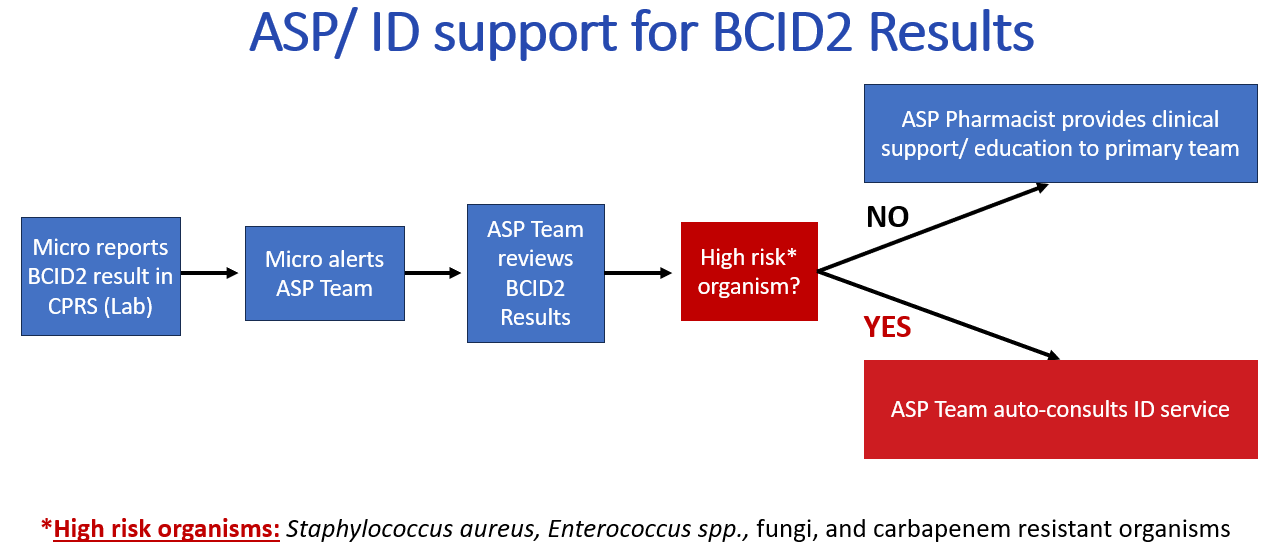
How is BCID2 incorporated into clinical practice?
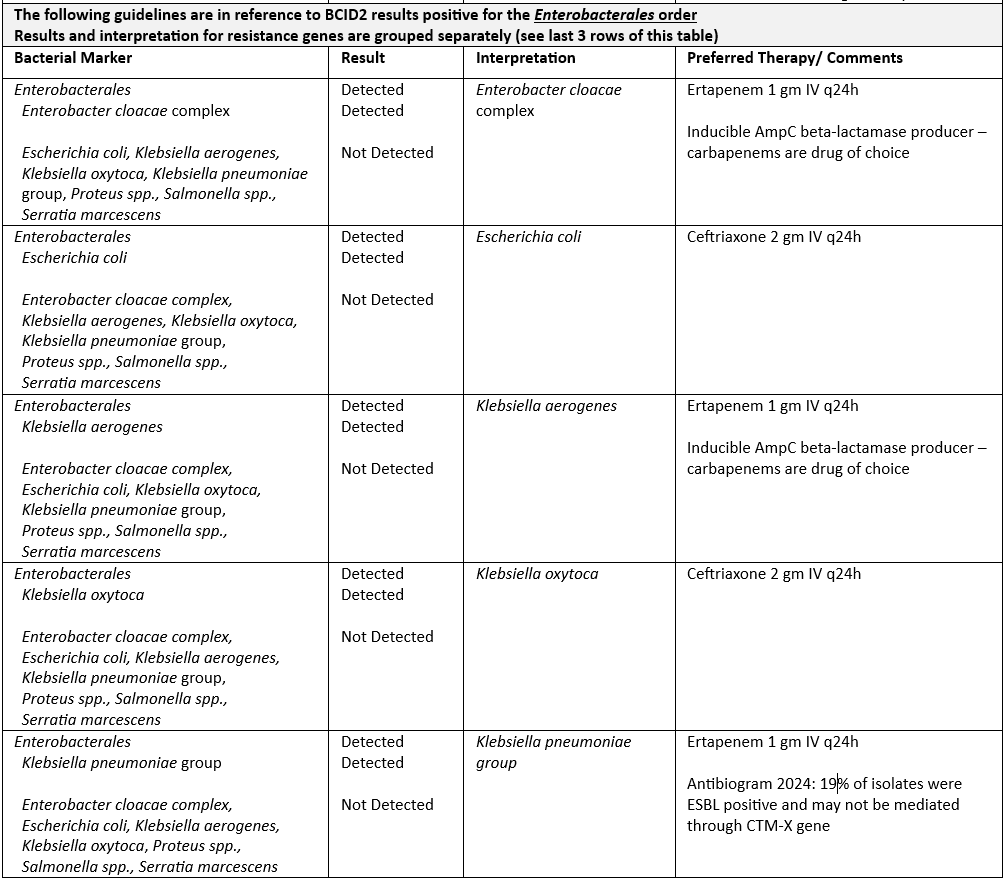
The microbiology lab notifies clinicians of positive blood culture gram-stain results immediately after they are performed. Afterwards, the BCID2 assay is performed for rapid identification. BCID2 results are typically available in CPRS within 2 hours. When blood culture gram stain and BCID2 results are known, current antimicrobial therapy should be evaluated considering the clinical picture and adjusted to the most appropriate single agent if possible. Recommended empiric antibiotic therapies for BCID2 results are outlined in Tables 2-4 for gram-positive bacteria, gram-negative bacteria, and fungi. The Antimicrobial Stewardship Team developed these recommendations based on an analysis of the institutional antibiogram and IDSA Clinical Guidelines. Contact the ASP Pharmacist for alternative recommendations if patient is not a candidate for first line therapy. All dosing recommendations assume normal renal or hepatic function, pleas adjust dosing accordingly.
How reliable are BCID2 results?
The BCID2 test is highly accurate in monomicrobial bacteremia (99% sensitivity and 99.8% specificity), but in the rare incidence of polymicrobial bacteremia it may be less accurate. Therefore, polymicrobial gram stain results and BCID2 results with multiple organisms detected should be interpreted with caution. On the other hand, certain infections may be polymicrobial in nature and the isolation of a single pathogen from blood cultures, while allowing narrowing of therapy, should not result in over-narrowing. An example would be complicated intra-abdominal infections where anaerobes are frequently present and therapy active against these pathogens should generally be included until definitive cultures of the site of infection have returned.
BCID2 identification is limited to the pathogens and resistance genes listed on the panel (Table 1). If a positive blood culture results in a negative BCID2 report, please contact ASP Pharmacist or ID team for guidance. Occasionally, the detection of a resistance gene does not equate to confirmation of resistance when susceptibility testing is performed. Standard susceptibility testing is required to determine final antimicrobial susceptibility and should be used to guide final therapy decisions. When full susceptibility results become available, therapy should be adjusted to the narrowest spectrum appropriate agent.
References:
1. Rhoads DD, Pournaras S, Leber A, et al. Multicenter Evaluation of the BIOFIRE Blood Culture Identification 2 Panel for Detection of Bacteria, Yeasts, and Antimicrobial Resistance Genes in Positive Blood Culture Samples. J Clin Microbiol 2023; 61(6): e0189122.